Multi-Point Merging Expression Syntax¶
The supported syntax for the processing logic expressions is described in the following table.
Expression Symbol |
Function |
Description |
|---|---|---|
$ |
Variable Selector |
The format is ${ variable }, in which variable can be a model, a measurement point, or an attribute of a model. |
if…else |
Conditional Statement |
If the condition is true, the statement runs a code. If the condition is false, the statement runs another code. The format of the statement is: if (condition) { run this code when condition is true } else { run this code when condition is false }. |
if…else if…else |
Conditional Statement |
Run one of multiple codes depending on the condition. The format of the statement is: if (condition 1) { run this code when condition 1 is true } else if (condition 2) { run this code when condition 2 is true } else { run this code when conditions 1 and 2 are false }. |
“::” |
Namespace Identifier |
Refer to the C++ syntax. The format of the statement is: class name (model) :: class member (measurement point / attribute). |
“+ - * /” |
Arithmetic Operators |
Arithmetic operators such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. |
“! && |” |
Logical Operators |
Logical operators like NOT, AND, OR. |
Note
Multi-Point Merging expressions support Scala syntax, but do not support loop statements like for and while.
Variable Autocomplete Feature¶
The automatic detection and completion of variables in the logic expression is enabled. When you write the logic expression, the system automatically detects all models, measurement points, and attributes in the organization. See the following example:
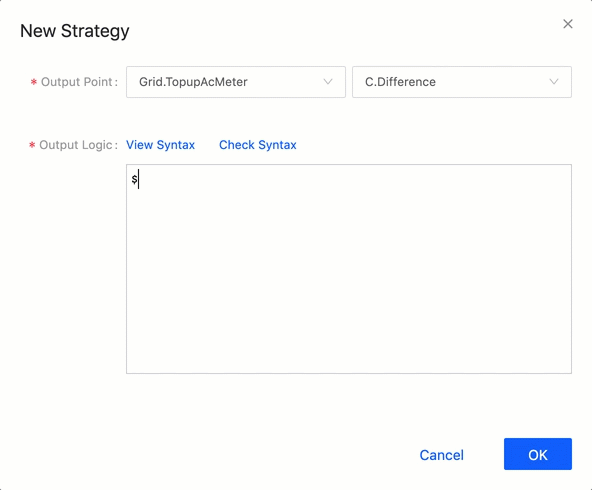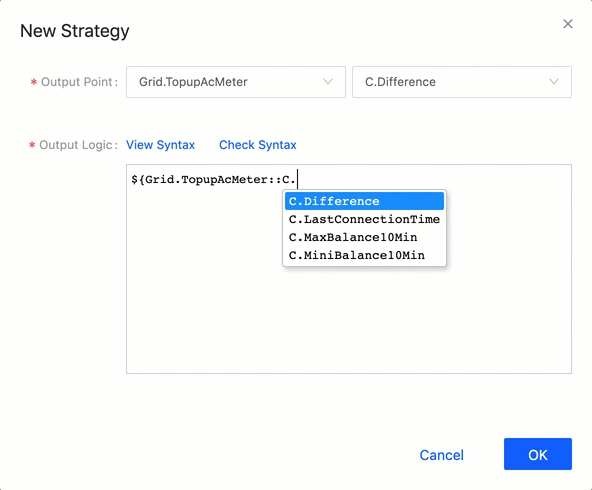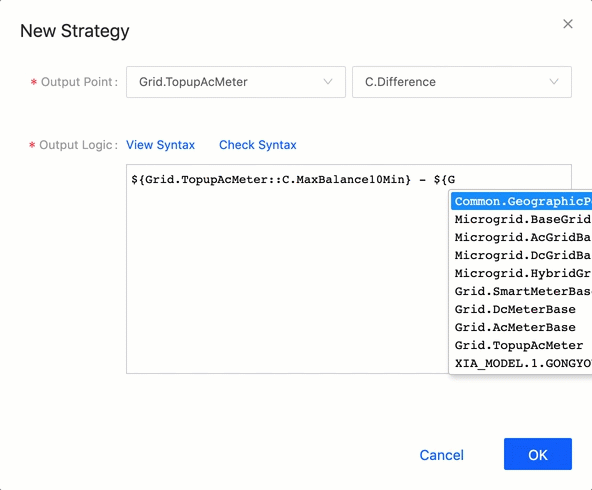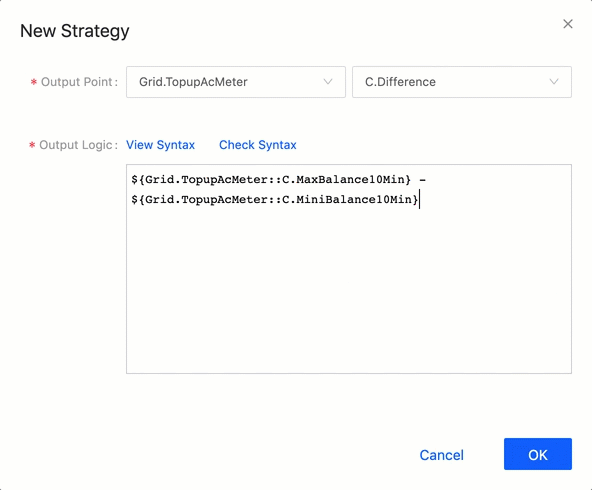
Expression Example¶
if(${turbine::wind_speed} > 50) {
${turbine::power}+10
}
else {
${turbine::power}-10
}
The function of the above expression is: If wind_speed is greater than 50, the output is power+10. Otherwise, the output is power-10.