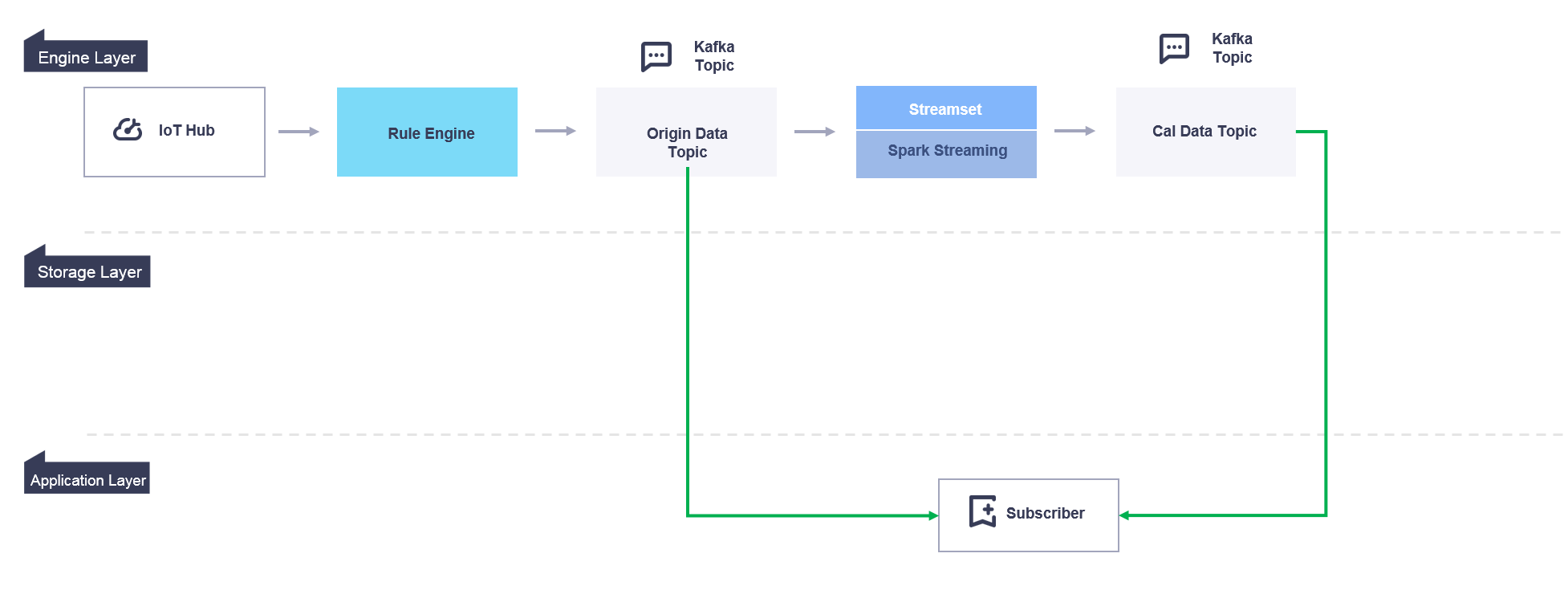
Real-time Data Flow¶
The real-time device data that is uploaded to EnOS will be processed and calculated by the EnOS stream data processing engine after flowing through the IoT hub. You can get an overview of the data flow on EnOS with the following figure:
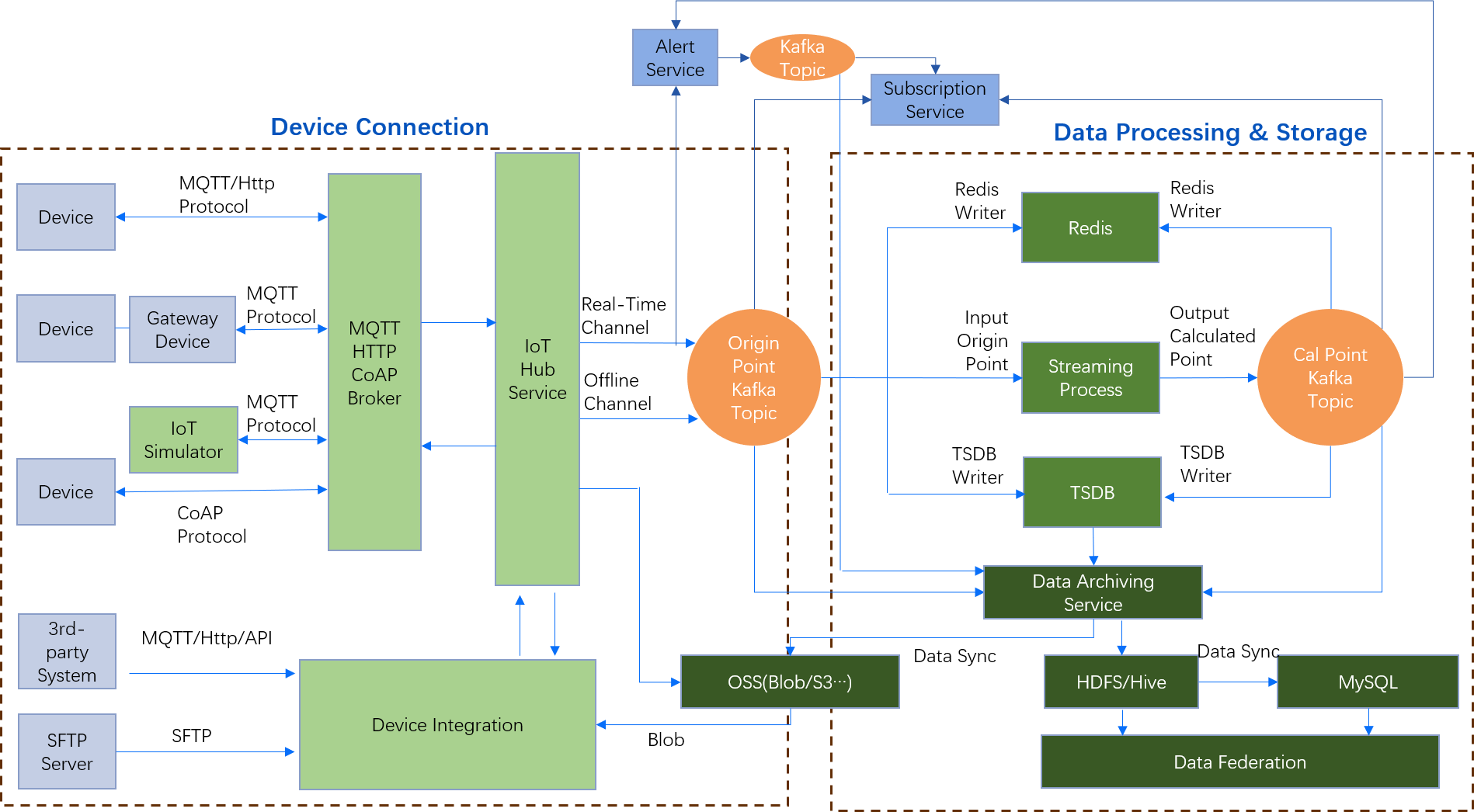
Real-time data that is processed by the EnOS Stream Processing Service can be viewed through 3 layers: the engine layer, the storage layer, and the application layer.
Engine Layer¶
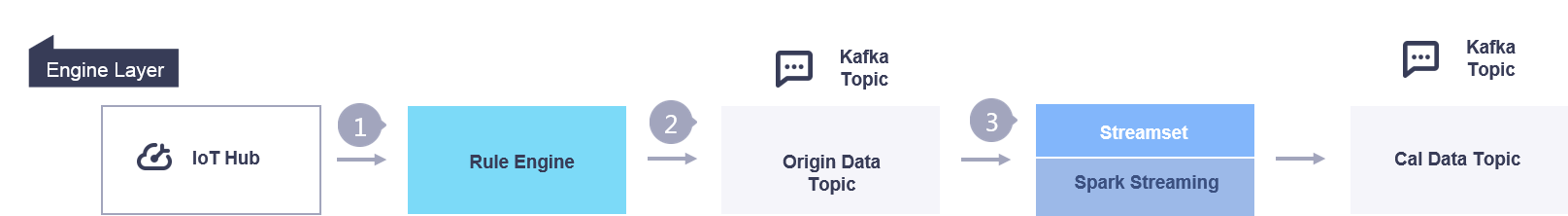
When assets are connected to EnOS Cloud, the asset raw data is ingested through the IoT Hub. After the data is ingested into the IoT Hub:
The Rule Engine routes the streams of data in Kafka message queue as topics.
The asset raw data is routed to the Origin Data Topic, and the data processed by the Streaming Engine is routed to the Cal Data Topic.
The Streaming Engine has two types of data processing logics.
User-defined logic: you can design real-time stream data processing jobs through the Stream Development function in the EnOS Management Console.
For more information about designing stream data processing jobs, see Developing Stream Processing Pipelines and Developing with Operators.
System logic: the system built-in logic that completes operations like data format conversion.
The following figure illustrates the data flow in the engine layer:
Storage Layer¶
EnOS provides a variety of data storage options based on data types and data reading requirements.
The EnOS Time Series Database is suitable for storing important and frequently-accessed data by data types. The data to be stored can be ingested from connected devices or integrated through the offline message channel. Asset AI type data, normalized AI type data, DI type data, PI type data, and generic data can be stored separately.
The Data Archiving service supports archiving business data that are huge in size and low in access frequency. The data to be archived can be ingested from connected devices or integrated through the offline message channel. The archived files will be synchronized to the target database and stored in the specified file path, thus achieving data backup.
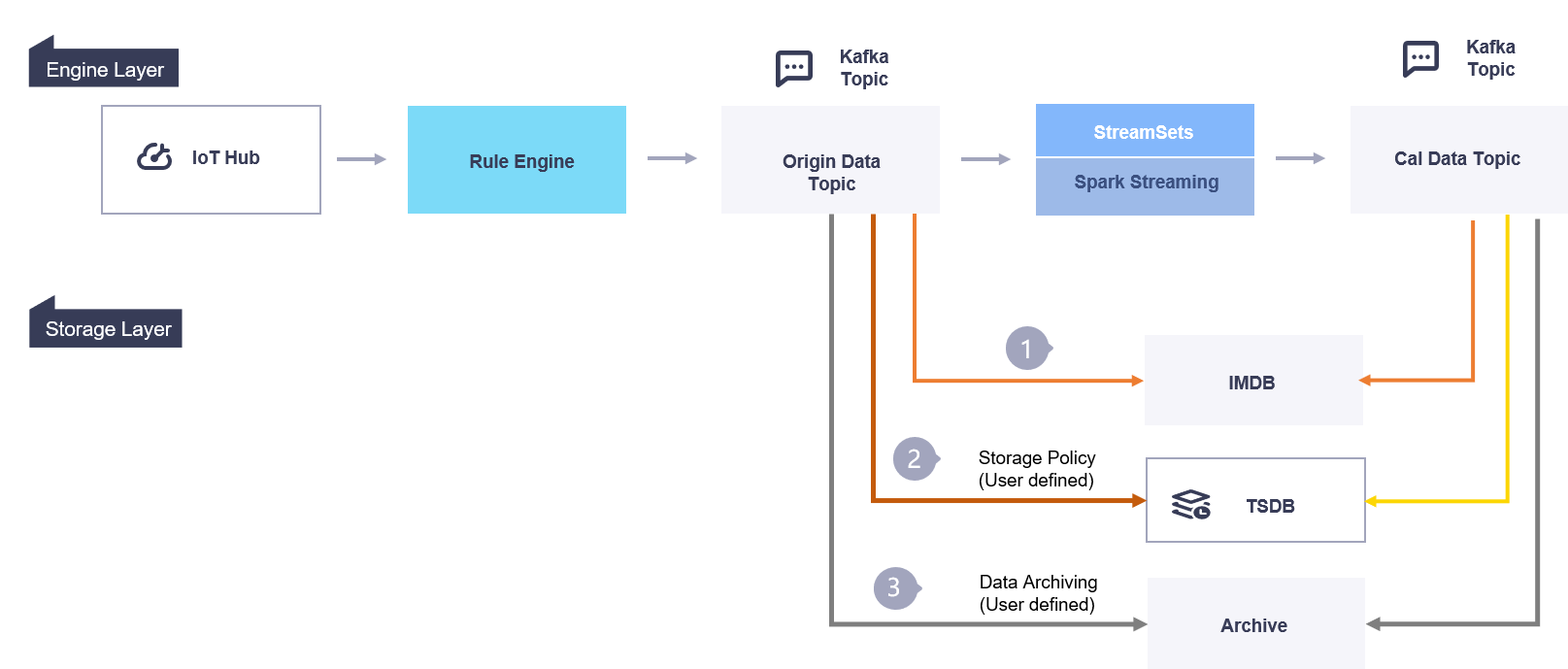
Data in the Origin Data Topic and the Cal Data Topic are written to In-memory Database (IMDB), Time Series Database (TSDB), and Data Archiving (Archive) storage.
IMDB: Stores only the latest data for fast query.
TSDB: Stores time series data of a specified time range based on the storage policies defined in the EnOS Management Console. The stored data can be retrieved through TSDB Data Service APIs.
Archive: Archives asset data based on the data archiving policy defined in the EnOS Management Console.
For more information about TSDB storage, see Configuring TSDB Storage. For more information about Data Archiving, see Configuring Data Archiving Jobs.
The following figure illustrates the data flow in the storage layer:
Application Layer¶
You can subscribe to both the original data and the calculated data so that the asset data can be consumed by your applications directly. The subscription settings can be configured through the Data Subscription service in the EnOS Management Console, where Java SDK can be used to retrieve the subscribed data. For more information about data subscription, see Developing Data Subscription Jobs.
The following figure illustrates the data flow in the application layer: