Key Concepts¶
Before you start the journey with EnOS, you need to learn about several key concepts.
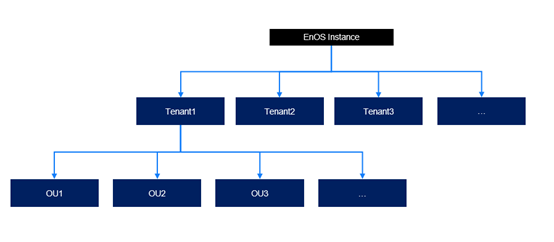
Tenant¶
The EnOS platform supports a two-tier management structure: tenants and organization units (OUs), enabling efficient management of enterprise resources and permissions. The “tenant” serves as the first-level management unit, typically representing an independent customer, enterprise, or higher-level entity using the IoT platform. Each tenant operates independently with its own data, users, and configurations.
Organization(OU)¶
An “Organization Unit (OU)” is the second-level management unit in the EnOS platform, serving as a logical grouping within a tenant, typically representing a department, unit, or branch. Organizations enable more effective management of users, resources, and devices within a tenant.
Resource¶
Resources within the IoT platform that support its service operations, such as time-series database storage resources for IoT data storage and computing resources for data analysis.
Device¶
A physical or virtual object connected to the IoT platform that can collect, transmit, and/or receive data. Examples can be wind speed sensors in the renewable energy sector, smart meters in buildings, and smoke sensors in factories.
Model¶
In EnOS, a model typically refers to a device model, which represents how a physical device can be described in the digital world. It defines the device’s static attributes, dynamic measurement points, associated services, and commands. EnOS leverages device models to digitally abstract similar devices from different manufacturers or models, enabling standardized configuration and management.
Asset¶
In the EnOS platform, an asset is a management object that can represent physical devices (e.g., solar panels or wind turbines) or entities comprising a group of assets (e.g., wind farms, buildings, or floors).
Asset Tree¶
A hierarchical structure organizing assets into parent-child relationships, allowing users to represent and manage complex systems or infrastructures (e.g., a grid of solar farms) more effectively.
Application¶
A software solution or tool built on the EnOS platform to perform specific functions, such as monitoring, analytics, or control of devices and assets.
Persona¶
Predefined user roles with specific permissions and responsibilities. Roles help simplify access management and ensure that users have the tools and data relevant to their tasks. The predefined user roles in EnOS Cloud include operation and maintenance management personnel, enterprise tenant management personnel, device access and management personnel, and application developers. For more information about the responsibilities of each role, see Predefined Roles.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)¶
A security mechanism that restricts system access to authorized users based on their assigned roles. RBAC ensures data security and operational efficiency.
Data Segregation¶
A secure resource organization approach that ensures data belonging to different tenants, organizations, or users is isolated and cannot be accessed by unauthorized parties.