Unit 3: Connecting the PC to EnOS™ and Ingesting Data¶
After the device modeling, device registration, and data storage policy configuration of the PC are completed in EnOS Console, you can now use the EnOS Java SDK for MQTT to connect the PC to EnOS and start ingesting data.
For detailed information about the EnOS Java SDK for MQTT, refer to the readme file on GitHub.
Step 1: Setting up the Development Environment¶
EnOS Java SDK for MQTT requires Java SE 8 and Maven 3. Take the following steps to set up your development environment.
Install JDK, which can be downloaded at https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html.
Install Maven, which can be downloaded at http://maven.apache.org/download.cgi.
Install a development environment, such as IntelliJ IDEA, which can be downloaded at https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/.
In the main
pom.xmlfile of your development project, add the EnOS Java SDK for MQTT as a dependency.<dependency> <groupId>com.enos-iot</groupId> <artifactId>enos-mqtt</artifactId> <version>2.2.16</version> </dependency>
In the main
pom.xmlfile of your development project, add oshi (an open source plug-in for ingesting computer operating system and hardware information) as a dependency.<dependency> <groupId>com.github.oshi</groupId> <artifactId>oshi-core</artifactId> <version>3.13.2</version> </dependency>
Step 2. Programming for Device Connection¶
After the development environment is set up, take the following steps to connect the PC to EnOS Cloud.
Declare the variables that will be used in the program.
private static final String uri = "tcp://{address}:{port}"; private static final String productKey = "product_key"; private static final String deviceKey = "device_key"; private static final String deviceSecret = "device_secret"; private static MqttClient client;
The
addressandportof the server varies according to the cloud region and instance. For private cloud instances, you can find the MQTT Broker address and port information by going to the EnOS Console Management and click Help > Environment Information.The
productKey,deviceKey, anddeviceSecretare the device properties generated when you registered the PC in Unit 1.
Declare the main function
connect()for initializing device connection.public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); }
Use the
connectfunction to connect the PC to EnOS Cloud.public static void connect() { System.out.println("Start connect with callback ... "); try { client = new MqttClient(uri, productKey, deviceKey, deviceSecret); // json device client.getProfile().setConnectionTimeout(60).setAutoReconnect(true); client.connect(new ConnCallback(){ public void connectComplete(boolean reconnect) { System.out.println("connect success"); } public void connectLost(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectLost"); } public void connectFailed(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectFailed : " + cause); } }); } catch (Throwable var1) { } System.out.println("connect result :" + client.isConnected()); }
Step 3. Programming for Ingesting Data and Uploading Data to EnOS Cloud¶
After the PC is connected to EnOS, take the following steps to ingest the PC system and hardware data and upload the data to EnOS Cloud.
Use the
collectDeviceInfo()function to ingest the PC system and hardware data.public static Map<String, Object> collectDeviceInfo() { oshi.SystemInfo si = new oshi.SystemInfo(); HardwareAbstractionLayer hal = si.getHardware(); OperatingSystem os = si.getOperatingSystem(); Map<String, Object> data=new HashMap<String, Object>(); data.put("system", os.toString()); data.put("model", hal.getComputerSystem().getManufacturer() + " " + hal.getComputerSystem().getModel()); data.put("cpu_core", hal.getProcessor().getLogicalProcessorCount()); data.put("cpu_used", hal.getProcessor().getSystemCpuLoad()); data.put("mem_total", hal.getMemory().getTotal()); data.put("mem_used", hal.getMemory().getAvailable()); data.put("cpu_used_average", hal.getProcessor().getSystemLoadAverage()); data.put("cpu_temperature", hal.getSensors().getCpuTemperature()); return data; }
Use the
updateAttribute()function to update the attributes of the PC device in the EnOS Management Console with the ingested system and hardware data.public static void updateAttribute(){ Map<String, Object> deviceInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); System.out.println("Computer info: "+deviceInfo); AttributeUpdateRequest request = AttributeUpdateRequest.builder() .setQos(1) .addAttribute("system", deviceInfo.get("system")) .addAttribute("model", deviceInfo.get("model")) .addAttribute("cpu_core", deviceInfo.get("cpu_core")) .addAttribute("mem_total", deviceInfo.get("mem_total")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Update Attribute: "+request); try { AttributeUpdateResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
Use the
postMeasurepointfunction to upload the ingested CPU load and memory usage data to EnOS Cloud.public static void postMeasurepoint(Map<String, Object> systemInfo) { MeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .addMeasurePoint("cpu_used", Double.parseDouble(systemInfo.get("cpu_used").toString())+0.0) .addMeasurePoint("mem_used", systemInfo.get("mem_used")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Measurepoint: "+request); try { MeasurepointPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
Step 4. Running the Program and Checking the Results¶
Compile and run the program for device connection and data ingestion.
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.ConnCallback; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.MqttClient; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.exception.EnosException; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.upstream.tsl.*; import oshi.hardware.HardwareAbstractionLayer; import oshi.software.os.OperatingSystem; public class Sample { private static final String uri = "tcp://{host}:{port}"; private static final String productKey = "product_key"; private static final String deviceKey = "device_key"; private static final String deviceSecret = "device_secret"; private static MqttClient client; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); updateAttribute(); } // Device connection initialization public static void connect() { System.out.println("start connect with callback ... "); try { client = new MqttClient(uri, productKey, deviceKey, deviceSecret); client.getProfile().setConnectionTimeout(60).setAutoReconnect(true); client.connect(new ConnCallback() { @Override public void connectComplete(boolean reconnect) { System.out.println("connect success"); } @Override public void connectLost(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectLost"); } @Override public void connectFailed(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectFailed : " + cause); } }); } catch (Throwable var1) { } System.out.println("connect result :" + client.isConnected()); } // Ingesting PC system and hardware data public static Map<String, Object> collectDeviceInfo() { oshi.SystemInfo si = new oshi.SystemInfo(); HardwareAbstractionLayer hal = si.getHardware(); OperatingSystem os = si.getOperatingSystem(); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<String, Object>(); data.put("system", os.toString()); data.put("model", hal.getComputerSystem().getManufacturer() + " " + hal.getComputerSystem().getModel()); data.put("cpu_core", hal.getProcessor().getLogicalProcessorCount()); data.put("cpu_used", hal.getProcessor().getSystemCpuLoad()); data.put("mem_total", hal.getMemory().getTotal()); data.put("mem_used", hal.getMemory().getAvailable()); data.put("cpu_used_average", hal.getProcessor().getSystemLoadAverage()); data.put("cpu_temperature", hal.getSensors().getCpuTemperature()); return data; } // Updating PC attributes with the ingested system and hardware data public static void updateAttribute(){ Map<String, Object> deviceInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); System.out.println("Computer info: "+deviceInfo); AttributeUpdateRequest request = AttributeUpdateRequest.builder() .setQos(1) .addAttribute("system", deviceInfo.get("system")) .addAttribute("model", deviceInfo.get("model")) .addAttribute("cpu_core", deviceInfo.get("cpu_core")) .addAttribute("mem_total", deviceInfo.get("mem_total")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Update Attribute: "+request); try { AttributeUpdateResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Uploading PC system data to EnOS Cloud public static void postMeasurepoint(Map<String, Object> systemInfo) { MeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .addMeasurePoint("cpu_used", Double.parseDouble(systemInfo.get("cpu_used").toString())+0.0) .addMeasurePoint("mem_used", systemInfo.get("mem_used")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Measurepoint: "+request); try { MeasurepointPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Check the running result of the program. The program will return the following sample result if the device connection is successful.
Start connect with callback ... connect result :true connect success Computer info: {mem_used=1401421824, cpu_used_average=-1.0, cpu_temperature=0.0, cpu_used=1.0, system=Microsoft Windows 10 build 17134, cpu_core=4, model=LENOVO 80T9, mem_total=8135401472} >>> Update Attribute: AnswerableMessageBody{id='null', method='thing.attribute.update', version='null', params={attributes={system=Microsoft Windows 10 build 17134, cpu_core=4, model=LENOVO 80T9, mem_total=8135401472}}} >>>Post Measurepoint: AnswerableMessageBody{id='null', method='thing.measurepoint.post', version='null', params={measurepoints={mem_used=1314672640, cpu_used=0.4697233989534014}, time=1565841030584}}
Check the status of the PC device in the Device List in the EnOS Management Console. The status of the device will change from
InactivetoOnline.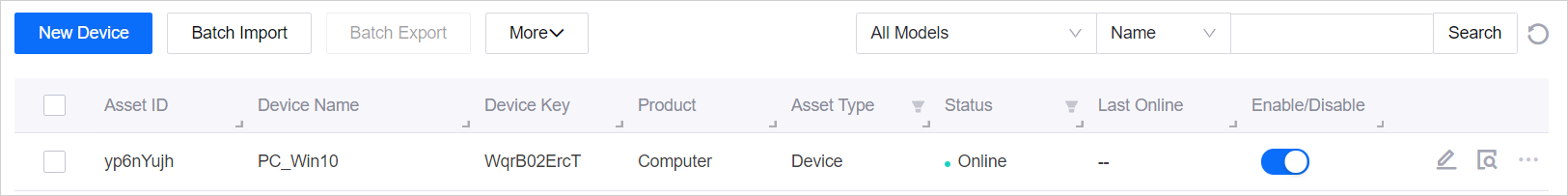
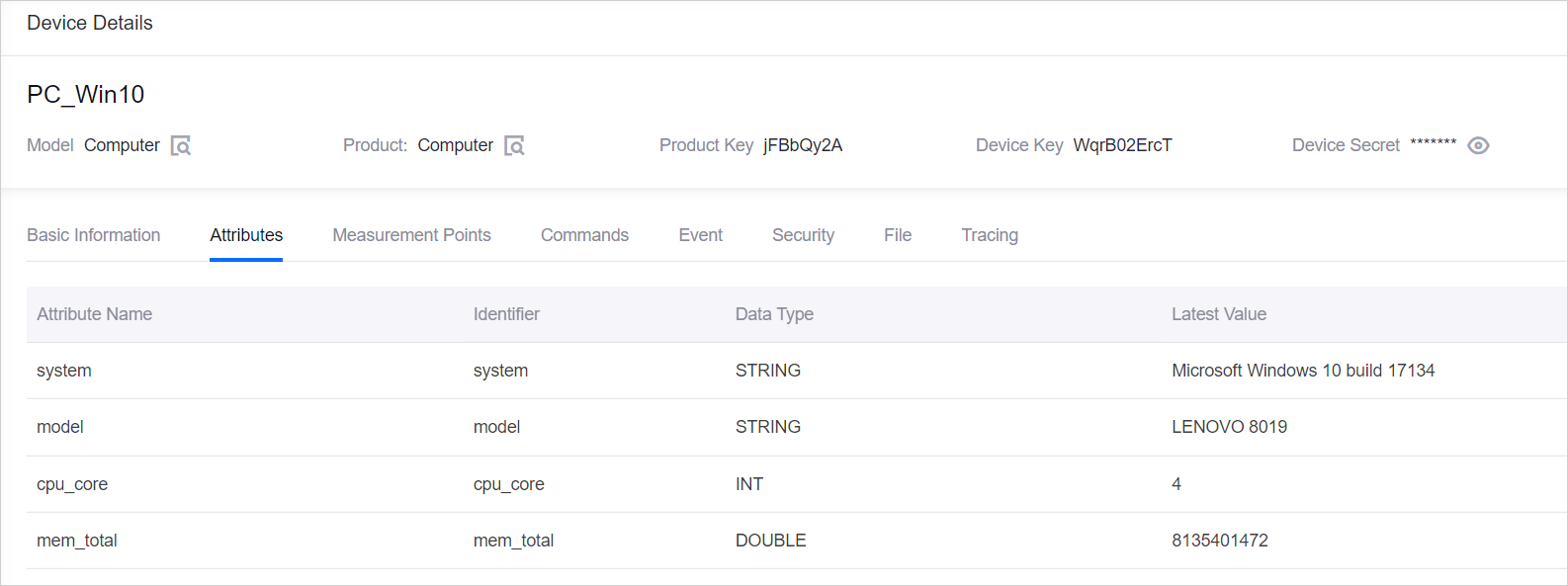
Check the updated attributes values of the PC device under the Attributes tab at the Device Details page.
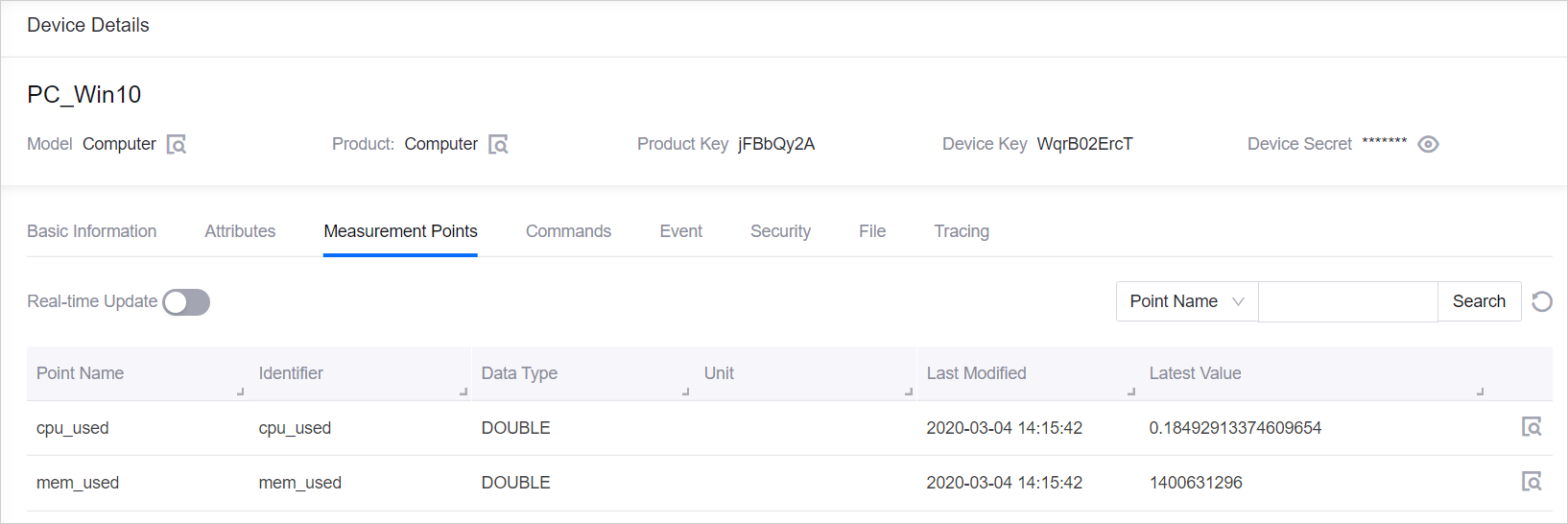
Check the data of the
cpu_usedandmem_usedmeasurement points that have been posted to the Cloud under the Measurement Points tab at the Device Details page.