Typical Deployment Modes¶
EnOS™ Edge supports the following deployment modes.
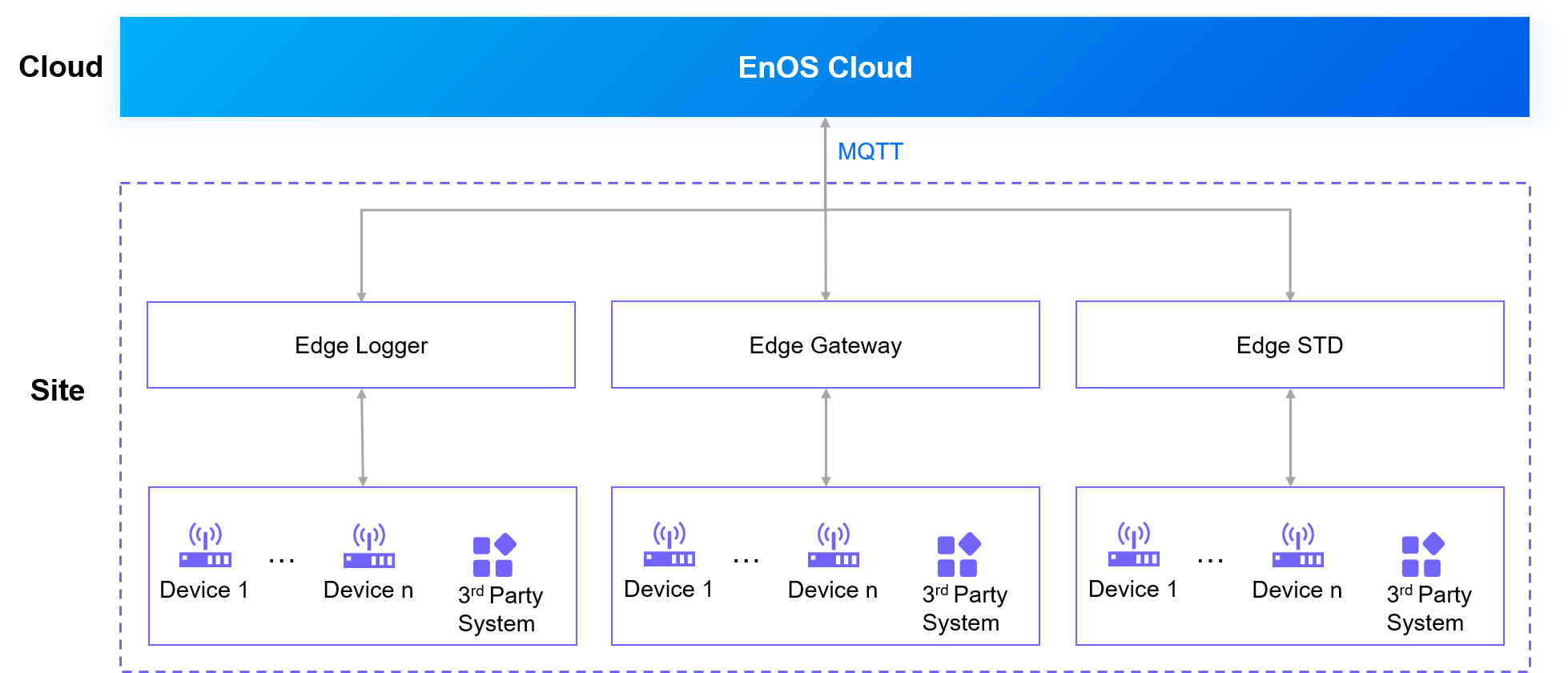
No Air Gap¶
Description¶
EnOS Edge communicates via a VPN link with the cloud through a firewall, and connects to a third-party system or sub-devices via Ethernet or a serial port.
Scenarios¶
Applies to scenarios where an EnOS Edge connects directly to the cloud.
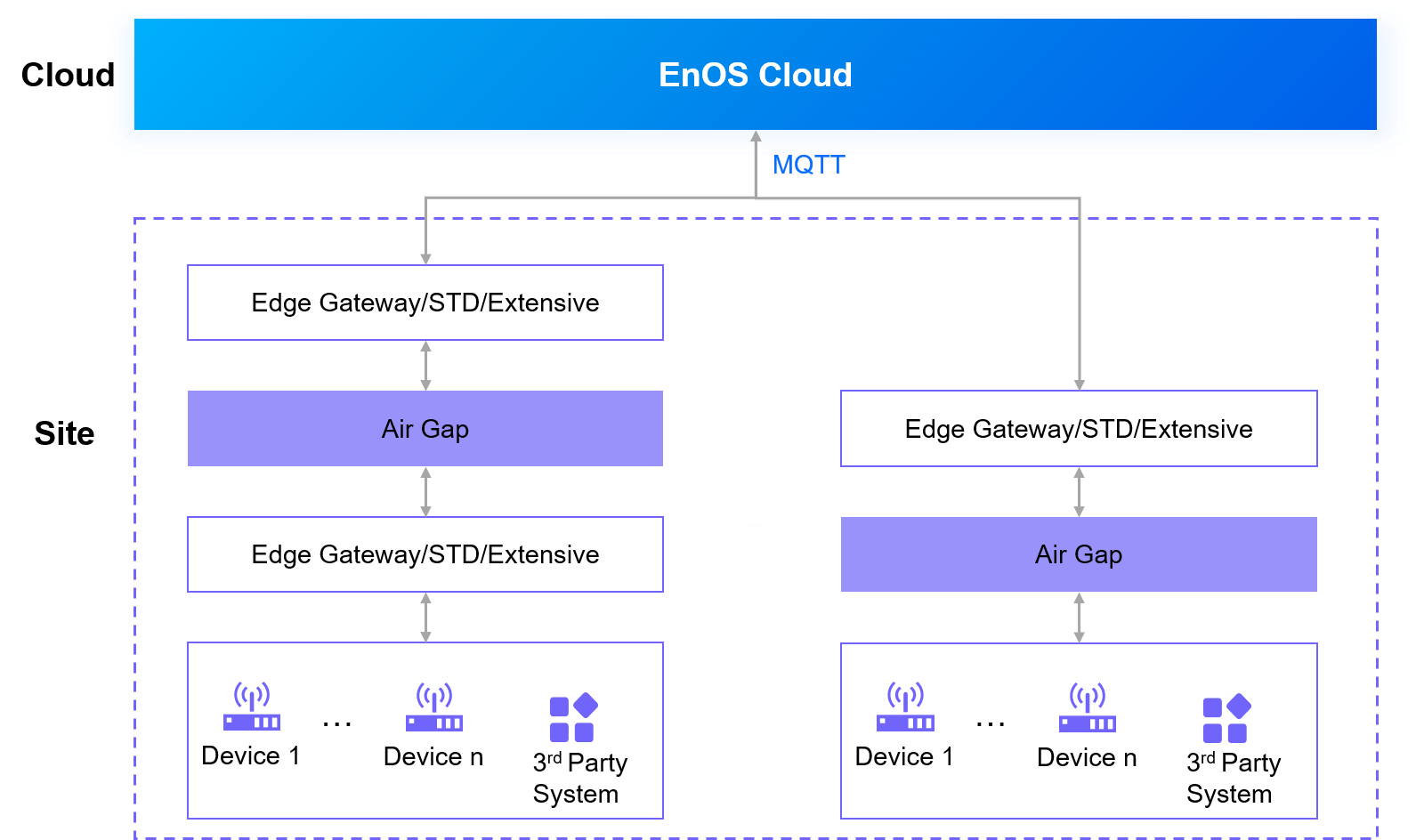
Air Gap on the Edge¶
Description¶
One EnOS Edge is deployed on the access-restricted side separated by an air gap, and connected to a third-party system or device over Ethernet or a serial port. The other Edge is deployed outside the access-restricted area, which is connected to the cloud via a VPN link through a firewall.
Scenarios¶
Applies to scenarios with high security requirements, such as centralized wind farms, or photovoltaic power plants.
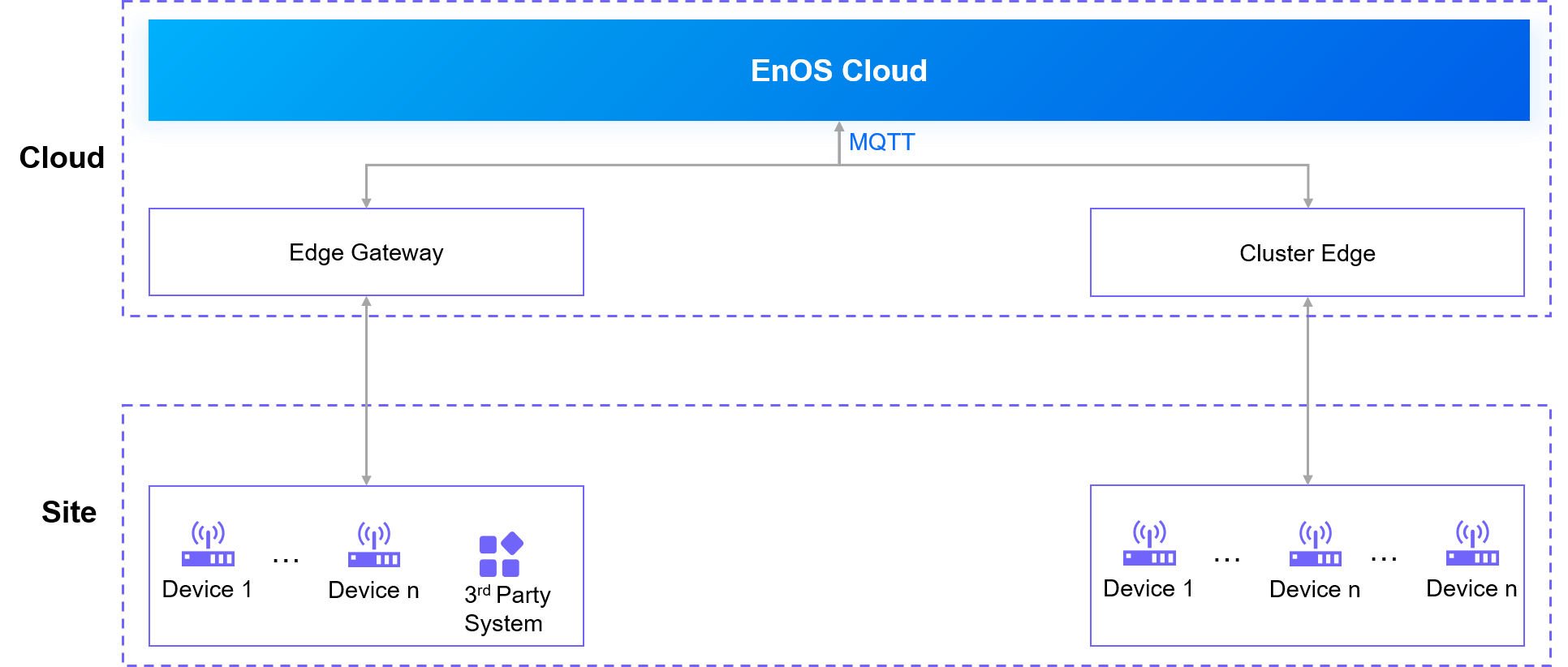
Cloud Edge¶
Description¶
An Edge Gateway is deployed on the cloud, which is connected to the third-party system or devices via a VPN link through a firewall using Ethernet.
Scenarios¶
Applies to scenarios where third-party systems or devices can be directly connected to EnOS, specifically those using industrial protocols, such as IEC104.
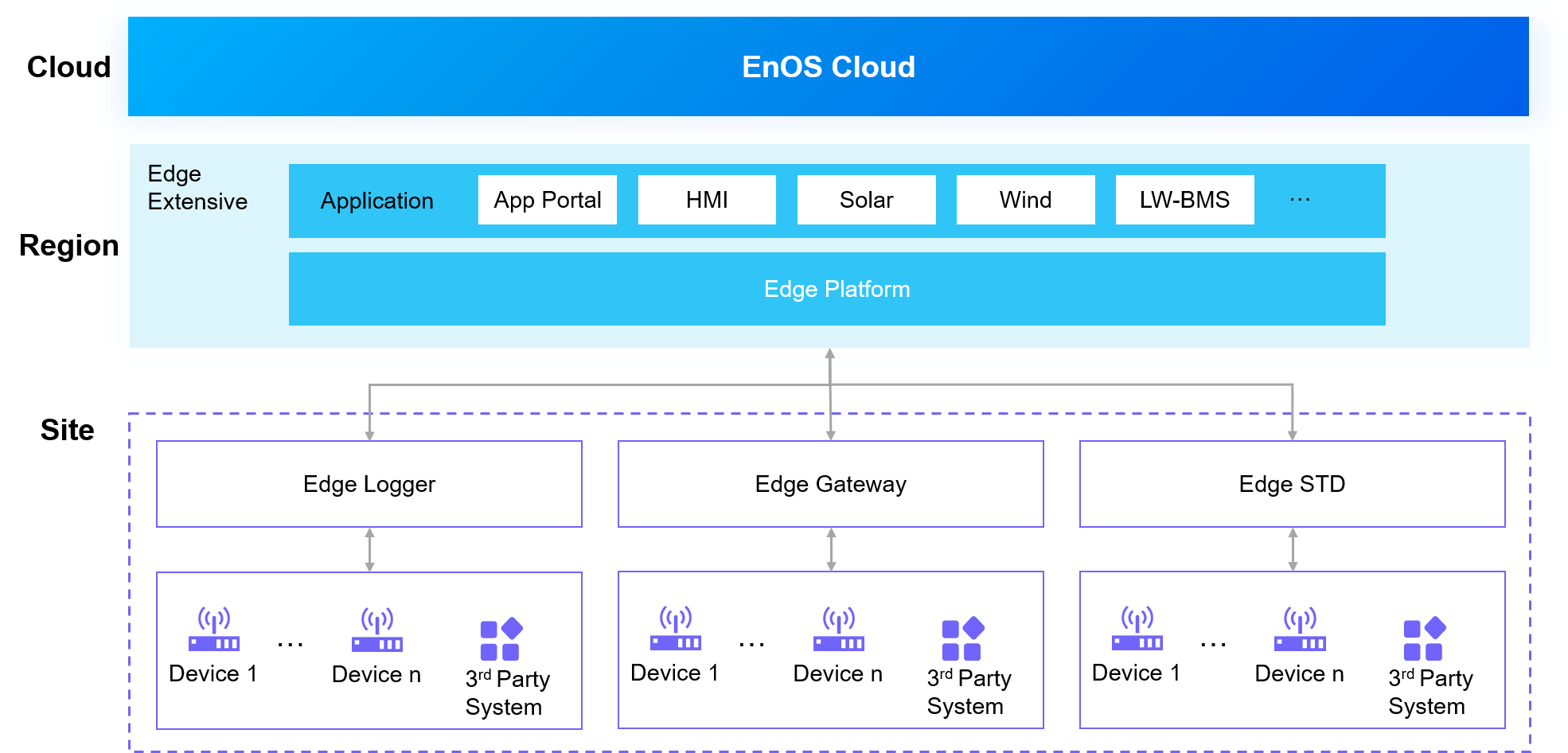
Edge at Regional Center¶
Description¶
An Edge STD or Extensive is deployed at a regional center, which is connected to Edge Loggers, Edge Gateways, Edge STDs, or third-party systems or devices via Ethernet, and communicates with the cloud via a VPN link through a firewall.
Scenarios¶
Applies to scenarios where a smart edge computing platform needs to be deployed at a regional center.