Explanation of Property Rule Expressions¶
Property rule expressions are used to define logical relationships between different properties and map property values within a single model or across multiple models.
For example, if the current model includes the attributes GenActivePW and Capacity, and you need to add a new property GenActivePWRatio, the value of GenActivePWRatio can be calculated using GenActivePW and Capacity. You can configure the following attribute expression for GenActivePWRatio:
"GenActivePW" * 100 / "Capacity"
Property expressions consist of three parts: properties (including attributes and measurement points), operators, and functions.
Property¶
When inserting a property, use the property identifier enclosed in double quotes, in half-width format. Property identifiers are case-sensitive.
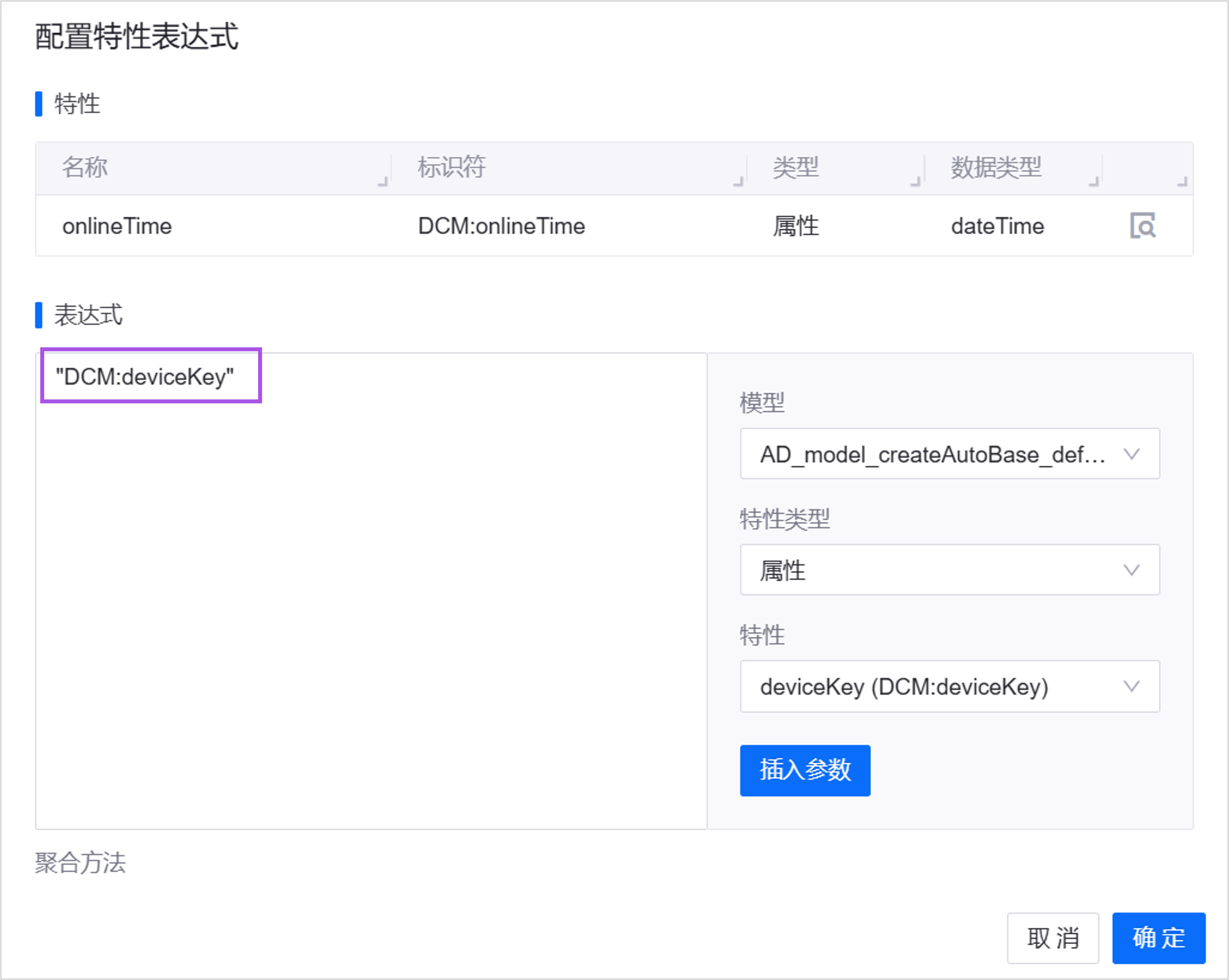
Operators¶
Category |
Operator |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Arithmetic |
3 + 2 |
Addition |
|
Arithmetic |
3 - 2 |
Subtraction |
|
Arithmetic |
3 * 2 |
Multiplication |
|
Arithmetic |
/ |
3 / 2.0 |
Division |
Arithmetic |
% |
3 % 2 |
Modulus |
Logical Operation |
> |
3 > 2 |
Greater than |
Logical Operation |
>= |
3 >= 2 |
Greater than or equal to |
Logical Operation |
< |
3 < 2 |
Less than |
Logical Operation |
<= |
3 <= 2 |
Less than or equal to |
Logical Operation |
= |
3 = 2 |
Equal to |
Logical Operation |
! = |
3 ! = 2 |
Not equal to |
Logical Operation |
and |
a > 1 and b > 2 |
And |
Logical Operation |
or |
a > 1 or b > 2 |
Or |
Conditional Judgment |
CASE |
CASE |
Ternary Expression |
Conditional Judgment |
COALESCE |
COALESCE(NULL, ‘a’, ‘b’) |
Returns the first non-null parameter |
Functions¶
Mathematical Functions¶
Category |
Function |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Numerical Handling Function |
ABS |
ABS(-2) |
Returns the absolute value |
Numerical Handling Function |
EXP |
EXP(2) |
Returns the value of e^x |
Numerical Handling Function |
FLOOR |
FLOOR(3.6) |
Rounds down |
Numerical Handling Function |
ROUND |
ROUND(1.5) |
Rounds to the nearest integer |
Numerical Handling Function |
CEILING |
CEILING(1.01) |
Rounds up |
Numerical Handling Function |
LN |
LN(2.7) |
Returns the natural logarithm with the base e, where e is approximately 2.71828 |
Numerical Handling Function |
LOG10 |
LOG10(100) |
Returns the base-10 logarithm |
Numerical Handling Function |
SQRT |
SQRT(3) |
Returns the square root |
Numerical Handling Function |
POWER |
POWER(2, 3) |
Performs exponentiation |
Numerical Handling Function |
RAND |
RAND() |
Returns a random number between 0 and 1 |
String Processing Function |
LENGTH |
LENGTH(‘abc’) |
Returns the number of characters in the string |
String Processing Function |
CONCAT |
CONCAT(‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’) |
Concatenates strings. If any parameter is null, the result is null |
String Processing Function |
LOWER |
LOWER(‘A’) |
Converts the string to lowercase |
String Processing Function |
UPPER |
UPPER(‘a’) |
Converts the string to uppercase |
String Processing Function |
TRIM |
TRIM(’ a ‘) |
Removes leading and trailing spaces from the string |
String Processing Function |
REPLACE |
REPLACE(‘acb’, ‘cb’, ‘e’) |
Performs string replacement. For example, REPLACE(‘acb’, ‘cb’, ‘e’) replaces ‘cb’ in ‘acb’ with ‘e’, resulting in ‘ae’ |
String Processing Function |
SUBSTRING |
SUBSTRING(‘abc’, 1, 2) |
Returns a substring. The parameters “1, 2” specify that the substring starts at the first character and has a length of 2, including the endpoints |
Time Processing Function |
CURRENT_DATE |
CURRENT_DATE |
Returns the current date |
Time Processing Function |
CURRENT_TIME |
CURRENT_TIME |
Returns the current time |
Time Processing Function |
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
Returns the current timestamp |
Time Processing Function |
YEAR |
YEAR(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the year |
Time Processing Function |
QUARTER |
QUARTER(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the quarter |
Time Processing Function |
MONTH |
MONTH(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the month |
Time Processing Function |
WEEK |
WEEK(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the week as a number between 1 and 53 |
Time Processing Function |
HOUR |
HOUR(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the hour |
Time Processing Function |
MINUTE |
MINUTE(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the minute |
Time Processing Function |
SECOND |
SECOND(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP) |
Returns the second |
Time Processing Function |
CONVERT_TZ |
CONVERT_TZ(‘2024-03-01 16:20:20’, ‘Asia/Shanghai’, ‘America/Los_Angeles’) |
Converts the first parameter from one timezone to another |
Time Processing Function |
FORMAT_DATE |
FORMAT_DATE(CURRENT_DATE, ‘yyyy-MM’) |
Formats the date |
Time Processing Function |
FORMAT_TIME |
FORMAT_TIME(CURRENT_TIME, ‘HH:mm’) |
Formats the time |
Time Processing Function |
FORMAT_DATETIME |
FORMAT_DATETIME(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, ‘yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm’) |
Formats the datetime |
Time Processing Function |
ADD_DATETIME |
ADD_DATETIME(‘QUARTER’, 1, ‘2024-03-01 16:20:20’) |
Performs a time offset operation |
JSON Processing Function |
JSON_VALUE |
JSON_VALUE(‘{“foo”: 100}’, ‘$.foo’)JSON_VALUE(‘[1, 2, {“x”: 3}]’, ‘$[2].x’) |
Extract the specified path expression from a JSON string |
Array Processing Function |
SPLIT_TO_STR_ARRAY |
SPLIT_TO_STR_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’, ‘,’) |
Splits the string into an array of strings, using a comma as the default delimiter. |
Array Processing Function |
SPLIT_TO_INT_ARRAY |
SPLIT_TO_INT_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’, ‘,’) |
Splits the string into an array of integers, using a comma as the default delimiter |
Array Processing Function |
ARRAY_SIZE |
ARRAY_SIZE(SPLIT_TO_STR_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’)) |
Calculates the length of the array |
Array Processing Function |
ARRAY_REMOVE |
ARRAY_REMOVE(SPLIT_TO_INT_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’), ‘>=’, 2) |
Removes elements from the array based on a condition. Supported operators include =, ! =, <, <=, >, >= |
Array Processing Function |
ARRAY_CONTAINS |
ARRAY_CONTAINS(SPLIT_TO_INT_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’), 3) |
Checks if the array contains the specified element |
Array Processing Function |
ARRAY_MAX |
ARRAY_MAX(SPLIT_TO_STR_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’, ‘,’)) |
Calculates the maximum value in the array |
Array Processing Function |
ARRAY_MIN |
ARRAY_MIN(SPLIT_TO_INT_ARRAY(‘1,2,3’, ‘,’)) |
Calculates the minimum value in the array |
Aggregation Functions¶
Aggregation functions support only property expressions of measurement point types.
Function |
Example |
Description |
|---|---|---|
SUM |
SUM(2) |
Calculates the sum |
AVG |
AVG(2) |
Calculates the average |
MIN |
MIN(2) |
Calculates the minimum value |
MAX |
MAX(2) |
Calculates the maximum value |
COUNT |
COUNT(2) |
Calculates the number of records |
Common Expression Templates¶
Commonly used expression templates are as follows.
Numerical Judgment¶
This template is commonly used to determine whether factors in an expression and their relationships conform to business logic. If the logic is not met, a default or null value is output.
When sum ("INV.AcPower") > sum("INV.DcPower"), the output is null. Otherwise, the output is (sum("INV.AcPower") * 100) / sum("INV.DcPower").
CASE WHEN (sum("INV.AcPower") > sum("INV.DcPower"))
THEN null
ELSE ((sum("INV.AcPower") * 100) / sum("INV.DcPower")) END
Null Value Conversion¶
This template is commonly used in scenarios involving multiple factors in summation to avoid the entire metric output being null due to a single null addend.
The COALESCE statement returns the first non-null parameter. For “COALESCE(sum(“INV.RecoverableProduction”), 0)”, if “sum(“INV.RecoverableProduction”)” is null, the output is 0. Otherwise, it returns the value of “sum(“INV.RecoverableProduction”)”.
(COALESCE(sum("INV.RecoverableProduction"), 0) + COALESCE(sum("INV.ActualProdLoss"), 0))
Enforced Aggregation¶
This template is commonly used in expressions where metrics involve multiple aggregation methods. It enforces summation aggregation, ignoring the default aggregation method of the original metric.
Even if the original metrics “SITE.Radiation2ACC” and “SITE.ConvertedCapacity” have other aggregation methods, the SUM expression first calculates “SITE.Radiation2ACC” * “SITE.ConvertedCapacity” and then sums the result.
SUM("SITE.Radiation2ACC" * "SITE.ConvertedCapacity") / SUM("SITE.ConvertedCapacity")
Aggregation Filtering¶
This template is used to filter out null values during the aggregation of multiple numeric values. If a single object has one or more null factors, it is excluded from the aggregation of multiple objects. If this syntax is not used, the default behavior is that an object is excluded from aggregation only when all its factors are null.
SUM(CASE
WHEN "Radiation2ACC" IS NULL OR "ConvertedCapacity" IS NULL
THEN NULL
ELSE "Radiation2ACC" * "ConvertedCapacity"
END)
/
SUM(CASE
WHEN "Radiation2ACC" IS NULL OR "ConvertedCapacity" IS NULL
THEN NULL
ELSE "ConvertedCapacity"
END)
JSON Parsing¶
This template extracts specific field values from JSON data. For instance, it can extract the value of ‘DELIVERY’ from the state attribute of an inverter to determine whether the device is currently in the “Delivered” state. It then returns a corresponding flag value (1 or 0).
CASE WHEN (json_value(max("INV.StateAttr"),'DELIVERY') ! = 0)
THEN 1
ELSE 0
END
Previous Period¶
This template can be used to query the data of the previous period. When the query period is Day(1)~Day(N), it is converted to Day(1-N)~Day(0) during the actual query. For example, if the query period for a metric is April 1 to April 5, 2024, adding LP updates the query period to March 27 to March 31, 2024.
LP(sum("ActiveProduction"))
Sequential Comparison¶
This template represents (current period metric / previous period metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
((sum("ActiveProduction") / LP(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)
Sequential Growth¶
This template calculates the sequential growth value by subtracting the previous period’s metric from the current period’s metric.
(sum("ActiveProduction") - LP(sum("ActiveProduction")))
Sequential Growth Rate¶
This template represents (current period metric - previous period metric / previous period metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
(((sum("ActiveProduction") - LP(sum("ActiveProduction"))) / LP(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)
Same Period Last Year¶
This template can be used to query the data of the same period last year. When the query period is Day(1)~Day(N), it is converted to the last year’s Day(1)~Day(N) during the actual query. For example, if the query period for a metric is April 1 to April 5, 2024, adding SPLY updates the query period to April 1 to April 5, 2023.
SPLY(sum("ActiveProduction"))
Year-over-Year Comparison¶
This template represents (current period metric / same period last year metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
((sum("ActiveProduction") / SPLY(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)
Year-over-Year Growth¶
This template calculates the year-over-year growth value by subtracting the same period last year’s metric from the current period’s metric.
(sum("ActiveProduction") - SPLY(sum("ActiveProduction")))
Year-over-Year Growth Rate¶
This template represents (current period metric - same period last year metric / previous period metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
(((sum("ActiveProduction") - SPLY(sum("ActiveProduction"))) / SPLY(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)
Same Period Last Month¶
This template can be used to query the data of the same period last month. When the query period is Day(1)~Day(N), it is converted to the last month’s Day(1)~Day(N) during the actual query. For example, if the query period for a metric is April 1 to April 5, 2024, adding SPLM updates the query period to March 1 to March 5, 2024.
SPLM(sum("ActiveProduction"))
Month-over-Month Comparison¶
This template represents (current period metric / same period last month metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
((sum("ActiveProduction") / SPLM(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)
Month-over-Month Growth¶
This template calculates the month-over-month growth value by subtracting the same period last month’s metric from the current period’s metric.
(sum("ActiveProduction") - SPLM(sum("ActiveProduction")))
Month-over-Month Growth Rate¶
This template represents (current period metric - same period last month metric / previous period metric) × 100. Multiplying by 100 facilitates direct display with a percentage sign (“%”) in the interface.
(((sum("ActiveProduction") - SPLM(sum("ActiveProduction"))) / SPLM(sum("ActiveProduction"))) * 100)