Unit 2: Configuring Alert Settings and Simulating Data Transmission¶
After the smart electric meter is registered on EnOS Console, you can connect the device and report simulated device data to EnOS Cloud. After that, configure alert settings to monitor the temperature value of the smart meter.
Step 1: Configuring alert settings¶
The Connecting Devices into EnOS Using SDK tutorial describes detailed steps for configuring alert settings for a device. Follow the same steps to configure alert setting for the temperature value of the smart electric meter.
See the following example:
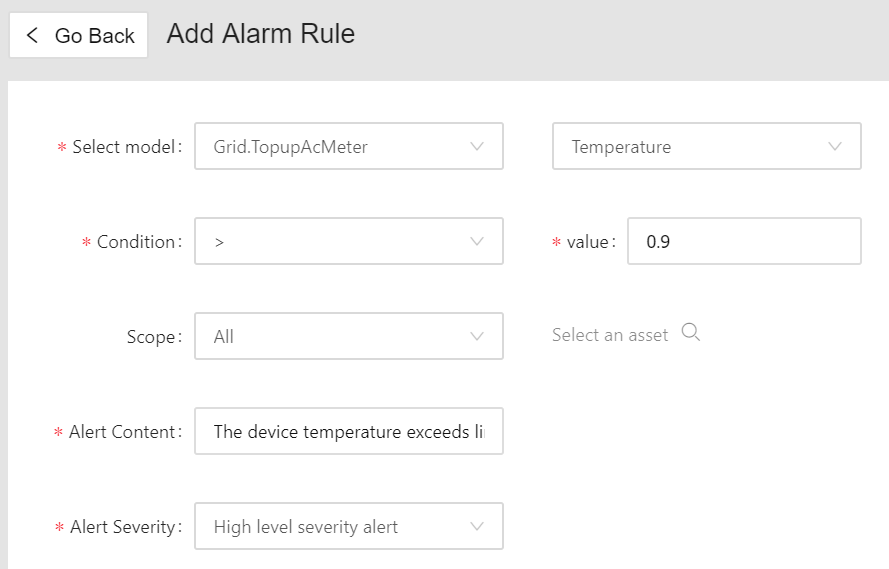
When the alert rule is saved, it will be running to monitor the temperature value of the electric meter. As soon as the temperature data is connected and exceeds the specified limit, the alert rule will be triggered, and an alert record will be generated.
Simulating device data¶
The Connecting Devices into EnOS Using SDK tutorial describes detailed steps for connecting a smart device into EnOS and simulating device data with the Device SDK for MQTT. Follow the same steps to report simulated temperature data of the electric meter to EnOS Cloud. The following code sample is for your reference:
import com.envisioniot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.IConnectCallback;
import com.envisioniot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.MqttClient;
import com.envisioniot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.exception.EnvisionException;
import com.envisioniot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.upstream.tsl.MeasurepointPostRequest;
import com.envisioniot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.sample.SimpleSendReceive;
import java.util.Random;
public class demo1 {
public static final String url = "tcp://{HOST}:{PORT}";
public static final String productKey = "{Product_Key}";
public static final String deviceKey = "{Device_Key}";
public static final String deviceSecret = "{Device_Secret}";
private static MqttClient client;
private static volatile boolean subDeviceLogined = false;
private static Random random = new Random();
private static int idInc = 20;
private static final char[] HEX_CHAR = new char[]{'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'};
public demo1() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
initWithCallback();
postMeasurepoint();
alwaysPostMeasurepoint();
}
public static void initWithCallback() {
System.out.println("start connect with callback ... ");
try {
client = new MqttClient(url, productKey, deviceKey, deviceSecret);
client.getProfile().setConnectionTimeout(60).setAutoReconnect(false);
client.connect(new IConnectCallback() {
public void onConnectSuccess() {
SimpleSendReceive.subDeviceLogin();
System.out.println("connect success");
}
public void onConnectLost() {
System.out.println("onConnectLost");
}
public void onConnectFailed(int reasonCode) {
System.out.println("onConnectFailed : " + reasonCode);
}
});
} catch (EnvisionException var1) {
}
System.out.println("connect result :" + client.isConnected());
}
public static void postMeasurepoint() {
Random random = new Random();
System.out.println("start post measurepoint ...");
MeasurepointPostRequest request = (MeasurepointPostRequest)MeasurepointPostRequest.builder().addMeasurePoint("Temperature", random.nextFloat()).build();
try {
client.fastPublish(request);
System.out.println(" post measurepoint success...");
} catch (Exception var3) {
var3.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void alwaysPostMeasurepoint() throws Exception {
while(true) {
long ts = System.currentTimeMillis();
postMeasurepoint();
System.out.println(client.isConnected() + " post cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - ts) + " millis");
Thread.sleep(10000L);
}
}
}
In this example:
- The variables
HOSTandPORTof the EnOS server vary with the cloud region and instance. For private cloud instances, contact your Envision project manager or support representative to get the host and port information. - The variables
productKey,deviceKey, anddeviceSecretare the triple attributes of the registered Demo_meter device, which can be found on the EnOS Console. - Randomly simulated values of the Temperature measuring point will be uploaded to EnOS Cloud every 10 seconds.
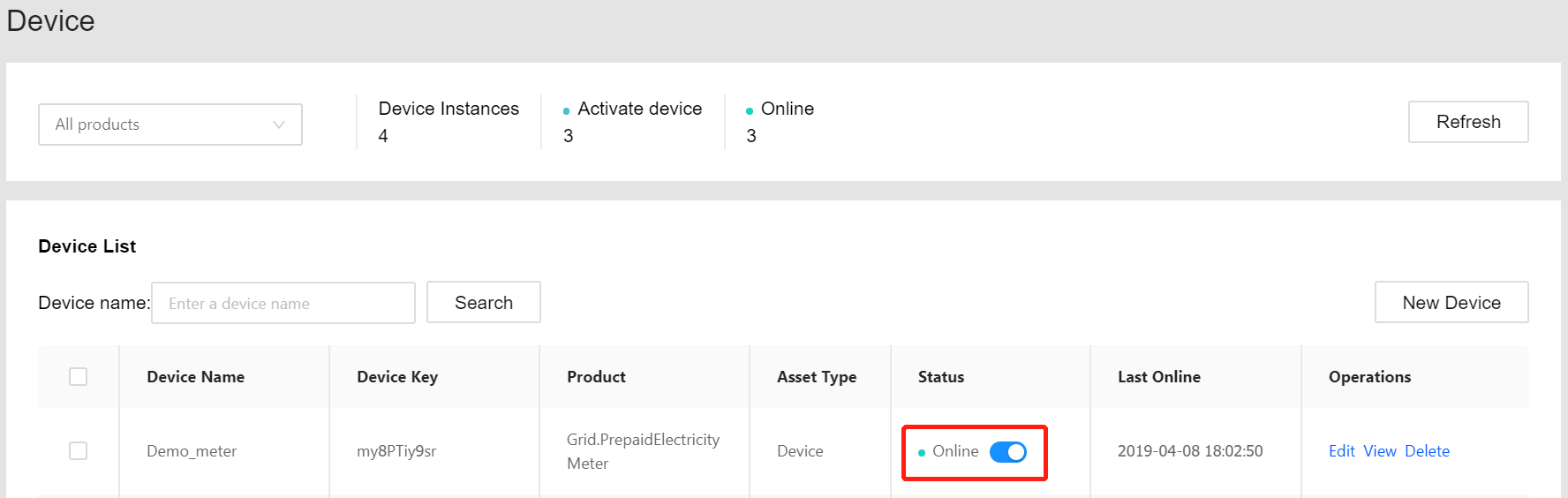
When the device is connected, check the device status through the Device Management > Device page:
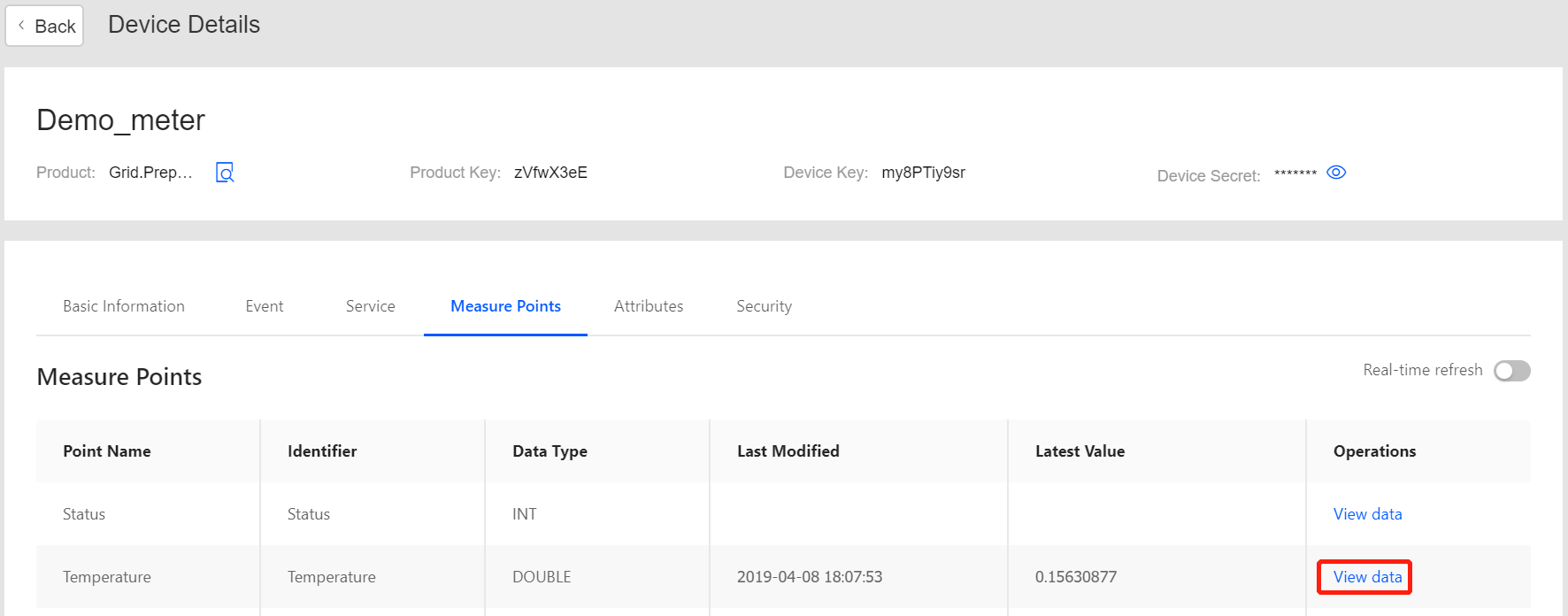
When simulated data is being uploaded to EnOS Cloud, view the uploaded data on the Device Details page: